Body composition is not about losing weight; it is about losing fat. You can lose weight while building muscle. It is called Body Composition.
This is when you want to modify your physique by burning fat while still increasing muscle. This technique is complex because it is not the same as merely losing weight.
It appears counterintuitive to lose body fat while building muscle. This is because a caloric deficit promotes weight loss, whereas to gain muscle, you must consume more calories than you expend. It is feasible to do both, but it involves fine-tuning your food and workouts. Everyday activities can also help with movement and calorie burning.
Here are some tried-and-true methods for approaching body recomposition and seeing success.
What exactly is body composition?
It is the ratio of fat mass vs. lean mass in your body. Body composition is sometimes used interchangeably with body fat percentage, but body fat percentage is only one component of your overall body composition.
Lean mass is a combination of muscle, bones, ligaments, tendons, organs, other tissues, and water – in other words, everything that isn’t fat. Depending on the method you use to calculate your body composition, water may appear as its own proportion.
What about body reshaping?
Body recomposition is the process of shifting your fat mass to lean mass ratio or reducing body fat while developing muscle mass. The goal of body recomposition is to simultaneously lose fat and grow muscle, as opposed to the typical strategy of “bulking and cutting,” in which you purposely gain a lot of weight (muscle and fat) and then go on an intensive calorie deficit to reduce the fat and reveal the muscle below.
Forget about losing weight.
You may maintain your present weight or even gain weight on a body recomposition plan; recall the phrase “muscle weighs more than fat”? This is just partially correct. Muscle has a higher density than fat.
Instead of weight, your physique alters throughout body recomposition. You may see the changes in your body as you proceed through body recomposition, such as an overall firmer appearance or that your clothes fit differently. When you are done with your body recomposition program, you may even gain weight but have a smaller physique.
For example, I currently weigh the same as I did before I began exercising and eating well. However, I wear smaller clothes and have better muscle tone than previously. I also feel a lot stronger than I did before I started a strength training regimen (a nonaesthetic benefit to body recomposition). So you can get rid of the scale because the scale can’t differentiate if you are losing fat or muscles and weight loss isn’t the primary goal of body recomposition.
However, there is one caveat to consider: if you wish to shed a significant quantity of body fat while not gaining much muscle mass, you may lose weight in the long run.
Body recomposition is a lengthy process, and you can’t treat this like a fad diet. Remember, you’re trying to do two things at once: shed fat and increase muscle. On their own, healthy weight loss and muscle gain take a long time: When you combine them, you’re in for the long haul. The process of body recomposition takes time to see the result, but it produces a long-term result.
What is the process of body recomposition?
Body recomposition is entirely dependent on your personal health and fitness objectives. Unlike typical weight-loss approaches, such as extremely low-calorie diets or periods of severe cardiac exercise, there is no set strategy for body recomposition.
There are certain general guidelines to follow. You must stick to the guideline to be successful in changing your body composition:
- Fat loss through cardiovascular activity.
- Muscle building with resistance (weight) training.
- To lose fat, reduce your calorie intake overall.
- Protein consumption should be increased to enhance muscle building.
How to Lose Fat
Fat loss is ultimately determined by your calorie intake. It will help if you consume fewer calories than you burn in order to lose weight. Cardiovascular exercise, or a combination of aerobic and resistance exercise, along with a nutritious diet, remains the best strategy for fat loss – there’s no getting past the research. Losing fat in a healthy and sustainable manner also entails setting realistic goals and not depriving your body of essential nutrients; disordered eating habits are never worth the risk.

How to Muscle Up
Focus on two primary variables for building muscle: weight exercise and protein ingestion. Strength training is vital for changing your body composition because your muscles will not grow if they are not challenged.
Furthermore, it would help if you took in more calories than you burn to encourage muscle growth. While all macronutrients are vital, protein is particularly important for muscle growth. Your body will struggle to repair muscular tissues that are broken down during weight training if you do not consume enough protein.
Studies show that a high-protein diet might aid in both fat loss and muscle gain. According to research, consuming more protein than you normally would when in a calorie deficit will assist preserve your lean body mass (a.k.a. muscle mass) more than being in a calorie deficit without modifying your protein intake.
Increasing protein intake and performing a rigorous weight-lifting routine leads to improvements in body composition in those who have already been following a strength training program.
Put everything together: Cycling for calories.
It may appear contradictory that you must consume fewer calories than you burn to reduce fat, yet you must eat more calories than you burn to build muscle. It’s actually rather simple once you understand the principle of calorie cycling: adjusting your calorie and macronutrient intake to match your daily objective.
The first step is to calculate your must-intake(maintenance calories) calories, that is, the calories you burn on days when you don’t exercise. You can get this amount from a licensed personal trainer, dietician, or other health professionals, or you can utilize an internet calorie calculator.
You should consume your maintenance calorie level on days when you conduct cardiac exercise. Consuming maintenance calories on a cardio day guarantees that you’re in a little deficit to stimulate fat loss, but not so much that your body begins to use muscle tissue as fuel. We need the muscle!
Eat more calories from protein-based food than your maintenance calorie on days when you complete a strength training program for 30 minutes or more. Depending on how much you want to gain muscle and how quickly, increase your maintenance calories by 5% to 15%.
On days when you don’t exercise, eat somewhat fewer calories than your maintenance calorie – by 5% to 10%. This is referred to as your “rest day calories.”
A weekly strategy to help you reach your body composition goals.
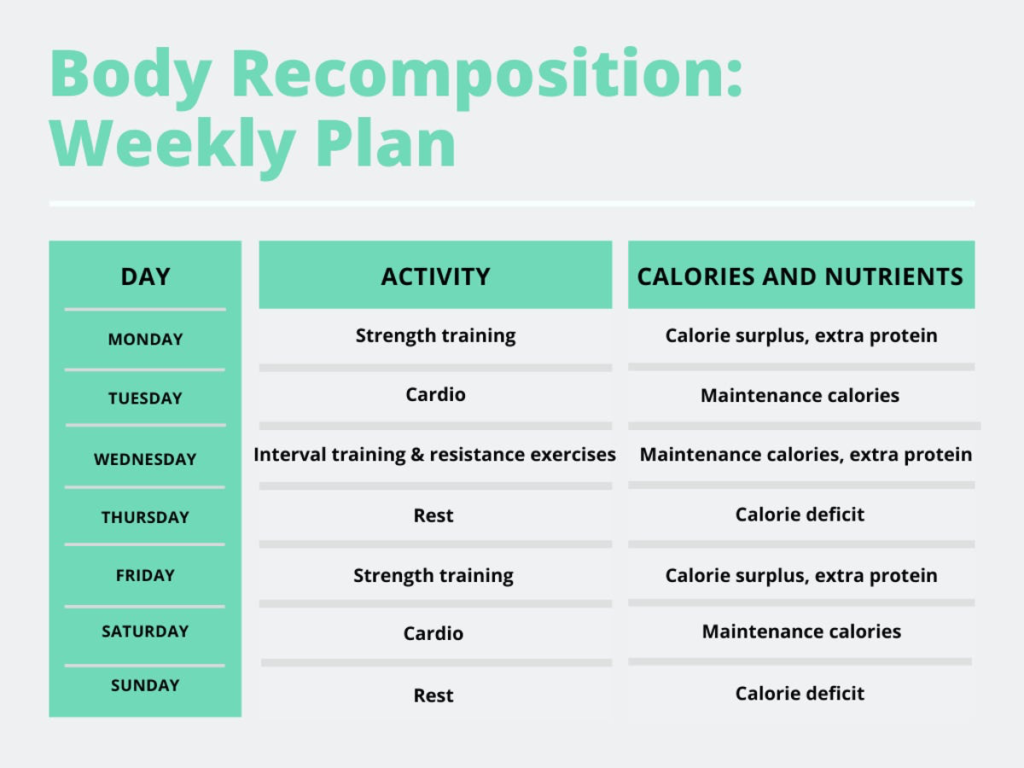
Consider the following: You ingest fresh calories every day, and your body must decide what to do with those calories. Your body has three main options: burn the calories immediately for fuel, repair and develop muscle tissue, or store them as fat.
You don’t want to retain calories as fat if you want to remodel your body. However, you want your body to employ additional calories to repair the muscles that were damaged during weight-lifting sessions.
In Conclusion
Improving your body composition is a popular objective that will have a positive result on your overall health. Protein consumption, a balanced exercise program, and a low-stress level all contribute to this development. We recommend you consult with your healthcare expert if you have any questions regarding your body composition or how to change it.

