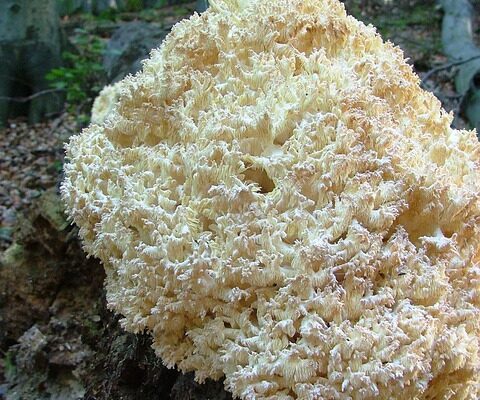
Lion’s mane mushrooms are huge, white, shaggy mushrooms that develop to resemble a lion’s mane. They include bioactive compounds that provide numerous health benefits for the body, including the brain, heart, and gut.
In many regions and countries in Asia, lion’s mane mushrooms have both culinary and medicinal purposes.
The following are nine health benefits of lion’s mane mushrooms and extracts, as well as dosages, preparation, and adverse effects.
1. Could help prevent dementia
As we age, our brain’s ability to expand and make new connections normally reduces, which may explain why many older persons’ mental competence deteriorates.
According to some studies and research, lion’s mane mushrooms contain hericenones and erinacines, two chemicals that can boost brain cell growth.
Based on some animal studies, researchers discovered that lion’s mane may help guard against degenerative brain illness that causes progressive memory loss, which leads to Alzheimer’s disease.

In addition, lion’s mane mushroom and its extracts have been found to lessen memory loss symptoms in rats and to prevent neuronal damage produced by amyloid-beta plaques, which build in the brain during Alzheimer’s disease.
A 2020 research of persons with mild Alzheimer’s disease discovered that taking 1 gram of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks improved cognitive test scores much more than a placebo.
It is crucial to emphasize, however, that the majority of the study has been done on animals or in test tubes. As a result, more human research is required.
Lion’s mane mushrooms contain chemicals that accelerate brain cell growth and protect them from Alzheimer’s disease-related damage. However, additional human-centered research is required.
2. Aids in the relief of mild depression and anxiety symptoms
Anxiety and sadness affect up to one-third of the population in affluent countries.
While there are numerous reasons for anxiety and depression, chronic inflammation may be a substantial influence.
Animal studies have revealed that lion’s mane mushroom extract contains anti-inflammatory properties that help alleviate anxiety and depression symptoms in mice.
In other animal studies, researchers discovered that lion’s mane extract helps rebuild brain cells and improve the functioning of the hippocampus, a part of the brain that controls emotional reactions and memory.
Researchers believe that better hippocampal functioning may account for the decreases in anxious and depressive behaviors observed in mice given these extracts.
While these animal trials are intriguing, there has been very little human study.
One small study of menopausal women published in 2010 discovered that eating cookies containing lion’s mane mushrooms every day for one month helped lower self-reported symptoms of annoyance and anxiety.
More research involving humans is needed to properly understand the association between lion’s mane mushrooms and minor symptoms of anxiety and depression.
3. Recovery from nervous system damage may be accelerated.
The nervous system is made up of the spinal cord, brain, and other nerves that run throughout your entire body. These components work together to send and receive signals that control nearly every body function.
Spinal cord or head injuries can result in a variety of negative medical effects. They frequently can lead to paralysis or loss of mental skills, and they can take a long time to cure.
However, studies have indicated that lion’s mane mushroom extract may assist in expediting recovery from these types of injuries by encouraging nerve cell growth and repair.
It may also assist in lessening the severity of brain damage following a stroke.
However, no human studies have been undertaken to evaluate whether lion’s mane has the same therapeutic impact on nervous system damage as animal research has revealed.
Although lion’s mane extract has been shown in many experiments to speed up healing from nervous system damage, human data is sparse.
A micronutrient test can determine your vitamin levels.
This micronutrient test looks for vitamin B12, vitamin D, vitamin E, magnesium, copper, selenium, and zinc. Get your findings from a certified laboratory in 2-5 days with free shipping.
4. It protects against stomach ulcers.
Ulcers can develop in the stomach, small and large intestines, and just about anywhere in the digestive tract.
Stomach ulcers are often caused by two key factors: proliferation of the bacterium H. pylori and stomach mucous layer damage caused by long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs).
By preventing the growth of H. Pylori, lion’s mane extract may provide protection against the development of stomach ulcers. Pylori and preventing stomach lining damage.
In addition, lion’s mane extract helps reduce inflammation and prevent tissue damage in various parts of the intestine. In fact, they may aid in illnesses such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
In a 2016 study of persons with ulcerative colitis, using a mushroom supplement containing 14% lion’s mane extract for three weeks considerably reduced symptoms and improved quality of life.
When the same trial was replicated in Crohn’s disease patients, the advantages were nearly the same as with placebo.
5. Lowers the risk of heart disease
The following are major risk factors for heart disease:
- obesity
- elevated triglyceride levels
- a significant level of oxidized cholesterol
- a greater proclivity to blood clots
According to research, lion’s mane extract can alter some of these parameters and lower the risk of heart disease.
Lion’s mane mushroom extract boosts fat metabolism and decreases triglyceride levels in rats and mice, according to research.
After a month, rats fed a high-fat diet and given daily dosages of lion’s mane extract had 27% lower triglyceride levels and 42% less weight gain, according to a 2010 study.
Both obesity and high triglycerides are risk factors for heart disease. Consuming lion’s mane mushrooms can help with heart health by preventing cholesterol oxidation.
Oxidized cholesterol molecules tend to thicken and harden arterial walls, which can lead to the risk of a heart attack or stroke. Reduced oxidation is good for your heart.
Also, lion’s mane mushrooms contain a chemical known as helicene B, which can slow blood clotting and reduce the risk of a stroke or a heart attack.
Lion’s mane mushrooms appear to assist the heart and blood arteries in a variety of ways, but human studies are needed to back this up.
Animal and test-tube research indicates that lion’s mane mushroom extract might reduce the risk of heart disease, but human studies are required to corroborate these findings.
6. Aids in the management of diabetes
Diabetes happens when the body’s capacity to regulate blood sugar levels is compromised. As a result, levels are always increased.
If you have high blood sugar levels, it can cause nerve damage in the hands and feet, loss of eyesight, and renal disease.
The lion’s mane mushroom may help with managing diabetes by increasing blood sugar control and lowering some of the adverse effects.
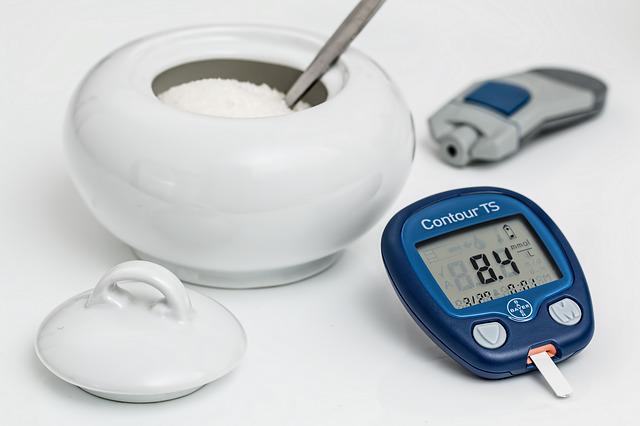
Some animal studies have demonstrated that lion’s mane can considerably lower blood sugar levels in both diabetic and normal mice.
At daily consumption as low as 2.7 mg/lb of body weight, lion’s mane mushroom decreases blood sugar levels by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme alpha-glucosidase, which breaks down carbohydrates in the small intestine.
When this enzyme is inhibited, the body is unable to digest and absorb carbohydrates as efficiently, resulting in decreased blood sugar levels.
Lion’s mane extract may decrease nerve discomfort in the hands and feet in addition to decreasing blood sugars.
Six weeks of daily consumption of lion’s mushroom extract reduced discomfort, lowered blood sugar levels, and even boosted antioxidant levels in diabetic nerve damage rats.
Although the lion’s mane mushroom has the potential to be utilized as a therapeutic diabetes supplement, additional research is needed to discover how it might be used in humans.
In rodents, lion’s mane mushroom can help lower blood sugar and relieve diabetic nerve pain, but further research is needed to discover how it affects humans.
7. Could assist in the fight against cancer
When your DNA is broken, cancer develops and leads your cells to divide and duplicate uncontrollably.
According to some research, the lion’s mane mushroom possesses cancer-fighting properties due to numerous of its unique components.
In fact, when a lion’s mane mushroom extract is combined with human cancer cells in a test tube, the cancer cells die more quickly.
However, at least one previous study failed to duplicate these findings.
Lion’s mane extract has been demonstrated to delay the spread of cancer as well as kill cancer cells.
There was a study done in a 2013 study of mice with colon cancer, consuming lion’s mane mushroom extract reduced disease metastasis to the lungs by 69%.
Another study published in 2014 discovered that lion’s mane extract was more successful than typical cancer treatments at reducing tumor growth in mice, as well as having fewer adverse effects.
However, because the anticancer properties of lion’s mane mushrooms have never been studied in humans, more research is required.
Animal and test-tube research reveals that lion’s mane extract can kill cancer cells and halt tumor spread, but human trials are still needed.
8. Reduces oxidative stress and inflammation
Many modern ailments, like cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders, are thought to be caused by inflammation and oxidative stress.
According to some studies, lion’s mane mushrooms have potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant components that may help lower the severity of several conditions.
In fact, according to a 2012 study that looked at the antioxidant properties of 14 different mushroom species, the lion’s mane had the fourth highest antioxidant activity and should be regarded as a good dietary source of antioxidants.
Some animal studies have found that lion’s mane extract reduces inflammation and oxidative stress indicators in rodents and may be especially beneficial in the treatment of liver damage, stroke, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Lion’s mane mushrooms have been proven to reduce the amount of inflammation released by adipose tissue, which may help minimize some of the health problems linked with obesity.
More research is needed to assess the possible health advantages in humans, but lab and animal findings seem promising.
9. Immune system booster
A powerful immune system defends the body from viruses, bacteria, and organisms that lead to disease.
As you are aware, a weak immune system can increase the body’s susceptibility to infectious infections.
According to animal studies, lion’s mane mushrooms can increase their immunity, which can protect the body against pathogens that enter their guts through the mouth or nose.
These effects could be explained in part by favorable alterations in gut flora that boost the immune system.
A 2012 study discovered that using lion’s mane extract on a regular basis virtually tripled the longevity of mice given a fatal dosage of salmonella germs.
Lion’s mane mushrooms have been proven to increase immunological function in rodents, although additional research is needed.

Dosage
There is no set dose for lion’s mane mushrooms. The safest and most helpful amount is determined by factors such as your age and overall health. You should consult with your doctor about the appropriate dosage for you.
Some researchers propose 3 – 5 grams per day to improve cognition.
A 2020 study found that taking three 350-mg lion’s mane capsules daily for 49 weeks significantly improved cognitive performance in adults aged 50 and older with mild Alzheimer’s disease symptoms.
According to a 2019 study, taking three 400-mg capsules daily for eight weeks helped improve melancholy, anxiety, and sleep difficulties in 77 adults who were overweight or obese.
The most efficient lion’s mane mushroom dose is determined by factors such as your age and overall health.
How to Prepare for a Lion’s Mane
Lion’s mane mushrooms can be eaten fresh, roasted, dried, or brewed into tea.
Many individuals describe the flavor as “seafood-like,” equating it to crab or lobster.
Cooked mushrooms can be used in meals such as risotto, spaghetti, and soup.
You can add Lion’s mane mushroom powder to hot water, tea, coffee, smoothies, or other drinks. It can also be used to season soups, stews, and gravies.
Raw, cooked, or dried lion’s mane mushrooms are all edible.
Forms
According to several researches, fresh lion’s mane mushrooms have the most health benefits. However, the cultivation methods may have an impact on the therapeutic characteristics of the mushrooms.
Lion’s mane mushrooms can be purchased over the counter in the following forms:
- tablets
- capsules
- powder
- tinctures
However, researchers warn that there are currently no criteria in place to ensure the safety and efficacy of these products.
Although fresh lion’s mane mushrooms are best, they can also be taken as a supplement in the form of tablets or capsules.
Side effects and safety
There has been no human research on the side effects after consumption of lion’s mane mushroom or its extract as of yet.
In rats, no deleterious effects were observed, even at doses as high as 2.3 grams/lb of body weight per day for one month or lower doses for three months.
However, because lion’s mane is a fungus, if you are allergic or sensitive to mushrooms, you should avoid it.
There have been documented incidents of persons developing skin rashes or having difficulties breathing after being introduced to lion’s mane mushrooms, which were most likely caused by allergies.
Animal studies indicate that lion’s mane mushrooms and extracts are extremely safe, even at large doses.
Commonly Asked Questions
Are lion’s mane mushrooms healthy?
Lion’s mane is used to treat a variety of health conditions, including lowering the risk of heart disease, increasing the immune system, and managing diabetes. More research, however, is required to establish these benefits.
Is it true that a lion’s mane mushroom improves memory?
Lion’s mane includes chemicals that may aid in nerve growth, and some studies have claimed that utilizing it may improve thinking and memory while also protecting against Alzheimer’s. More research, however, is required.
Is lion’s mane mushroom beneficial for ADHD?
Lion’s mane is used to treat ADHD because of its ability to protect and improve brain function. There is, however, no scientific evidence to support its practice.

Is it illegal to own a lion’s mane mushroom?
It is permissible to purchase and utilize a lion’s mane. However, because of its scarcity, it is a protected species in various nations and states in the United States, making foraging unlawful. If you intend to forage for a lion’s mane, check with your local rules first, and always buy a lion’s mane from a reliable and sustainable source.
To Conclude
Lion’s mane mushrooms and extracts have been demonstrated to provide a variety of health advantages.
Some studies found that lion’s mane mushrooms may help prevent dementia, alleviate minor symptoms of anxiety and sadness, and repair nerve damage.
It has also been found in animal studies to have powerful anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties, as well as to reduce the risk of heart disease, cancer, ulcers, and diabetes.
While present research appears encouraging, further human studies are needed to establish practical health applications for lion’s mane mushrooms.
